LLDPE Plastic
In the world of plastics, Linear Low-Density Polyethylene, or LLDPE, often operates quietly in the background, but its significance cannot be overstated. While it may not always take the spotlight like some of its flashier plastic counterparts, such as PET or HDPE, LLDPE is an indispensable material found in an array of products that touch our lives daily. In this article, we’ll explore the versatile world of LLDPE, delving into its diverse applications and highlighting its essential role in various industries.
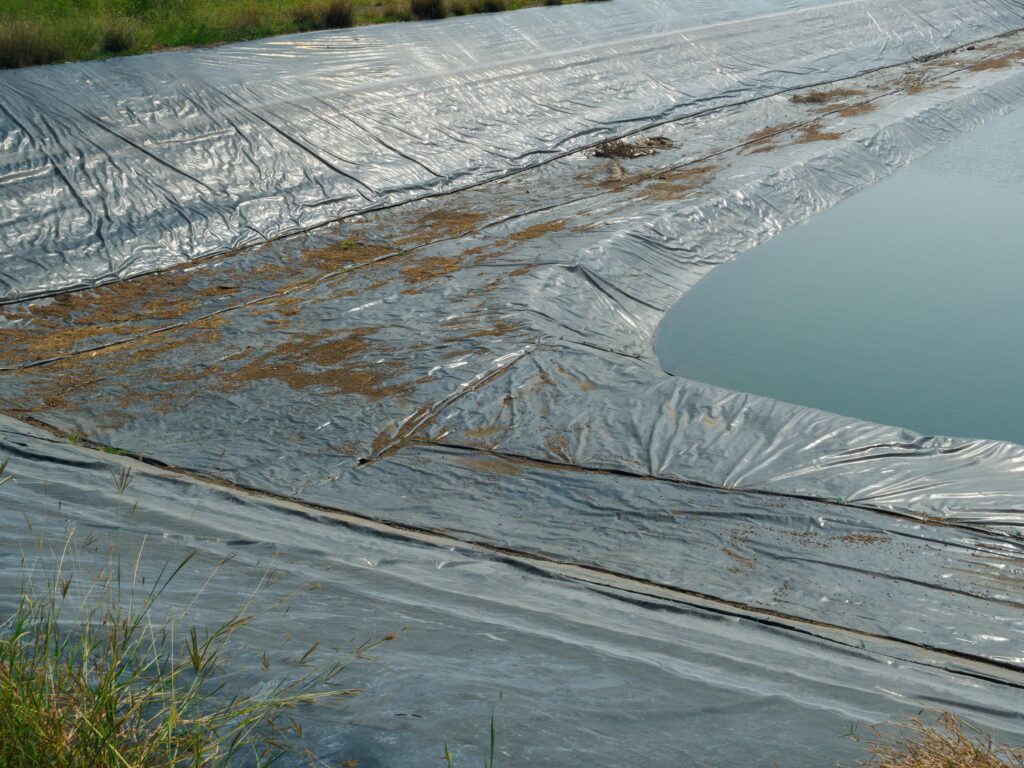


The history of Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) is a story of innovation and the relentless pursuit of improving the properties and applications of plastics. LLDPE’s origins can be traced back to the mid-20th century when the plastics industry was undergoing a significant transformation.
Birth of Polyethylene
The story begins with the invention of polyethylene in the 1930s by Reginald Gibson and Eric Fawcett, researchers at the Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) in the United Kingdom. However, the initial form of polyethylene, known as Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE), had limitations, such as low tensile strength and high branching, which restricted its use in certain applications.
The breakthrough came in the late 1950s when two scientists, Ziegler and Natta, developed a revolutionary catalyst that allowed for the production of polyethylene with a more linear and less branched structure. This discovery gave birth to LLDPE, a new type of polyethylene with improved properties.
Commercialization
The commercial production of LLDPE began in the 1960s, with the first major manufacturer being the Dow Chemical Company. LLDPE’s exceptional flexibility, toughness, and resistance to environmental stress cracking quickly made it a sought-after material in various industries.
One of LLDPE’s early successes was in the realm of packaging materials. Its unique properties, such as excellent heat-sealing and film-forming capabilities, revolutionized the production of plastic bags and flexible packaging. This led to the widespread use of LLDPE in retail, food, and pharmaceutical packaging.As the plastics industry continued to evolve, LLDPE found applications in agriculture, construction, and consumer goods. LLDPE geomembranes became essential for environmental containment in landfills and construction projects. In agriculture, LLDPE films played a pivotal role in crop protection and irrigation.
With increasing environmental concerns, the recyclability of LLDPE became a focus of attention. Efforts to improve the recyclability of LLDPE products have led to more sustainable practices in the industry. Over the years, research and development have led to even more specialized forms of LLDPE with enhanced properties. These innovations have expanded its applications further, making it a versatile material in the modern world.
Understanding Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE)
LLDPE is a thermoplastic polymer made from the polymerization of ethylene molecules, with a branched structure that imparts unique properties. This material is renowned for its exceptional flexibility, toughness, and resistance to impact and environmental stress cracking. LLDPE can be processed in various forms, including films, sheets, and molded parts, making it a versatile choice for a wide range of applications.
The Remarkable Versatility of LLDPE
LLDPE’s versatility extends across numerous industries:
1. Packaging Materials: LLDPE is a staple in the packaging industry. It’s used for manufacturing flexible films and bags, providing excellent puncture resistance and sealing properties. LLDPE’s durability ensures the safe packaging of food, pharmaceuticals, and more.
2. Agricultural Uses: LLDPE films play a crucial role in agriculture, serving as greenhouse covers and mulch films. They help regulate temperature, conserve water, and improve crop yield.
3. Construction: LLDPE geomembranes are used for environmental containment in construction projects, preventing soil and water contamination. Additionally, LLDPE pipes are employed in water distribution and drainage systems.
4. Rotomolding: LLDPE’s ease of processing makes it ideal for rotomolding applications, producing items such as storage tanks, playground equipment, and industrial containers.
5. Consumer Goods: LLDPE’s toughness and flexibility make it a preferred choice for manufacturing various consumer goods, including toys, trash bins, and furniture.


The Environmental Advantage
LLDPE offers several environmental benefits:
1. Recyclability: Like other polyethylene materials, LLDPE is recyclable, contributing to a more sustainable approach to plastics.
2. Lightweight: LLDPE’s lightweight nature reduces transportation costs and fuel consumption during shipping, lowering carbon emissions.
3. Durability: Its resistance to environmental stress cracking ensures a long lifespan for products, reducing the frequency of replacements and conserving resources.
4. Agricultural Efficiency: LLDPE films used in agriculture help conserve water and reduce the need for chemical pesticides, promoting eco-friendly farming practices.
A Material for a Sustainable Future
In conclusion, Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) may not always grab the headlines, but its significance is undeniable. From packaging our groceries to protecting the environment in construction and agriculture, LLDPE quietly but indispensably supports our modern way of life. Its versatility, toughness, and eco-friendly attributes make it a vital material across various industries. The next time you encounter an LLDPE product, take a moment to appreciate the unsung heroes that help make our world more efficient, resilient, and environmentally responsible.















Looking for custom plastic fabrication? Why not check Industrial Plastics, Australia’s Premier Plastic Fabricator!
